Tungsten alloys, known as heavy alloys, are 90–97% tungsten with other metals added to increase the alloy’s ductility. Tungsten alloys are determined by manufacturers separately and cannot be standardized like steel or aluminum alloys. Therefore, there is no real naming standard for them. Tungsten alloys have the greatest melting point of any metal, good high-temperature strength, excellent creep resistance, great thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and electron emission performance. Read More…
When you need specialty metals, run of the mill products or hard to find alloys contact Metal Associates. We are a full line distributor of metals such as aluminum. These include aluminum strip, aluminum bar, aluminum rods, 6061 aluminum, 7075 aluminum, aluminum coil, aluminum sheet, aluminum pipe, aluminum plate & aluminum tubing. We offer quality customer service & high quality products.

Elmet Technologies LLC is a 100% US owned and operated, fully integrated manufacturer of molybdenum, tungsten products and alloys. Elmet produces both flat and long/round mill products, including plate, sheet, and foil, flat rolled products, rod and wire. We have industry leading machining, fabrication, and assembly capabilities. We are a specialty metals business with over 85 years of molybdenum ...
At All Metal Sales Inc., we take pride in delivering high-quality tungsten to meet the demanding needs of industries that require exceptional strength and performance. We specialize in sourcing and distributing tungsten in a variety of forms, from raw materials to precision-engineered components, ensuring our customers receive products that excel in durability, heat resistance, and density.

At H. Cross Company, we pride ourselves on being a leading force in the fabrication and supply of precision tungsten components. With decades of experience behind us, we’ve built our reputation on the strength, reliability, and unmatched performance of our tungsten products. We understand the critical role this refractory metal plays across a wide range of demanding applications—from...

At Buffalo Tungsten, we take pride in being a leading manufacturer of high-purity tungsten powder and related products for customers around the world. We specialize in producing tungsten powders that meet the precise requirements of industries where performance, consistency, and purity are critical.

More Tungsten Alloy Suppliers

Types of Tungsten Alloys
Tungsten Nickel Copper
The tungsten nickel-copper alloys have great mechanical strength and excellent electrical conductivity and are simple to produce. They can shield from radiation and have great thermal stability. Tungsten nickel-copper alloys are less ductile than nickel-iron alloys. However, they are not magnetic, making them a good substitute in some contexts. Oncology instruments, electrical sensor shields, guidance system components, and military technology use tungsten nickel copper.

Tungsten Carbide
The most significant tungsten alloy is tungsten carbide. It is also known as a tungsten-cobalt alloy because it consists of tungsten, carbon, and cobalt. Tungsten carbide (also referred to as "industrial teeth") is hard, strong, and corrosion-resistant. Cutting tools, blades, cobalt tools, and wear-resistant components are all made with carbide.
Carbide is currently used extensively in the aerospace and military industries. Demand will continue to increase with future developments of high-tech weaponry and technology.
Tungsten Nickel Iron Alloy
Tungsten nickel-iron alloys are superior in ductility, strength, and density. These alloys can endure extremely high temperatures, have good machining properties, and have a thermal conductivity five times greater than die and punch steels. If these alloys are intended to be used in magnetism-sensitive procedures, such as medical imaging equipment, it is crucial to understand that iron makes them magnetic. Tungsten nickel-iron alloys are resistant to elastic deformation and, therefore, ideal for glass-to-metal sealing. These alloys work well for radiation shielding, ballasts, bearing assembly, defense applications, and balance weights.
Applications of Tungsten Alloys
- Permanent magnets: Tungsten steel is used to create permanent magnets. A metal's or alloy's magnetic characteristics are highly sensitive to microstructure. When tungsten is present in steel in these proportions, for instance, it stabilizes the martensite phase, which has higher ferromagnetism than the ferrite (iron) phase due to its greater resistance to magnetic domain wall motion, although tungsten is not a ferromagnetic element.
- Industry: Tungsten is primarily used to manufacture tungsten carbide (WC), one of the toughest carbides. Tungsten carbide is used by metalworking, woodworking, mining, petroleum, and construction industries to create wear-resistant abrasives and cutting instruments such as knives, drills, circular saws, dies, milling, and turning tools. About 60% of the world's tungsten consumption is currently attributed to this industrial use.
- Jewelry: The jewelry industry produces rings made of sintered tungsten carbide, tungsten carbide/metal composites, and metallic tungsten. Nickel is used as the metal matrix in WC/metal composite rings rather than cobalt because it takes on a higher sheen when polished. Tungsten carbide is ceramic, even though producers and merchants occasionally refer to it as a metal. Rings constructed of tungsten carbide are exceptionally abrasion resistant and will maintain a burnished polish longer than rings made of metallic tungsten. However, tungsten carbide rings are fragile and may break when struck hard.

Choosing the Proper Tungsten Alloy Supplier
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing tungsten alloys from a tungsten alloy supplier, it is important to compare at least 4 to 5 suppliers using our tungsten alloy directory. Each tungsten alloy supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each tungsten alloy company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple tungsten alloy companies with the same form.









 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
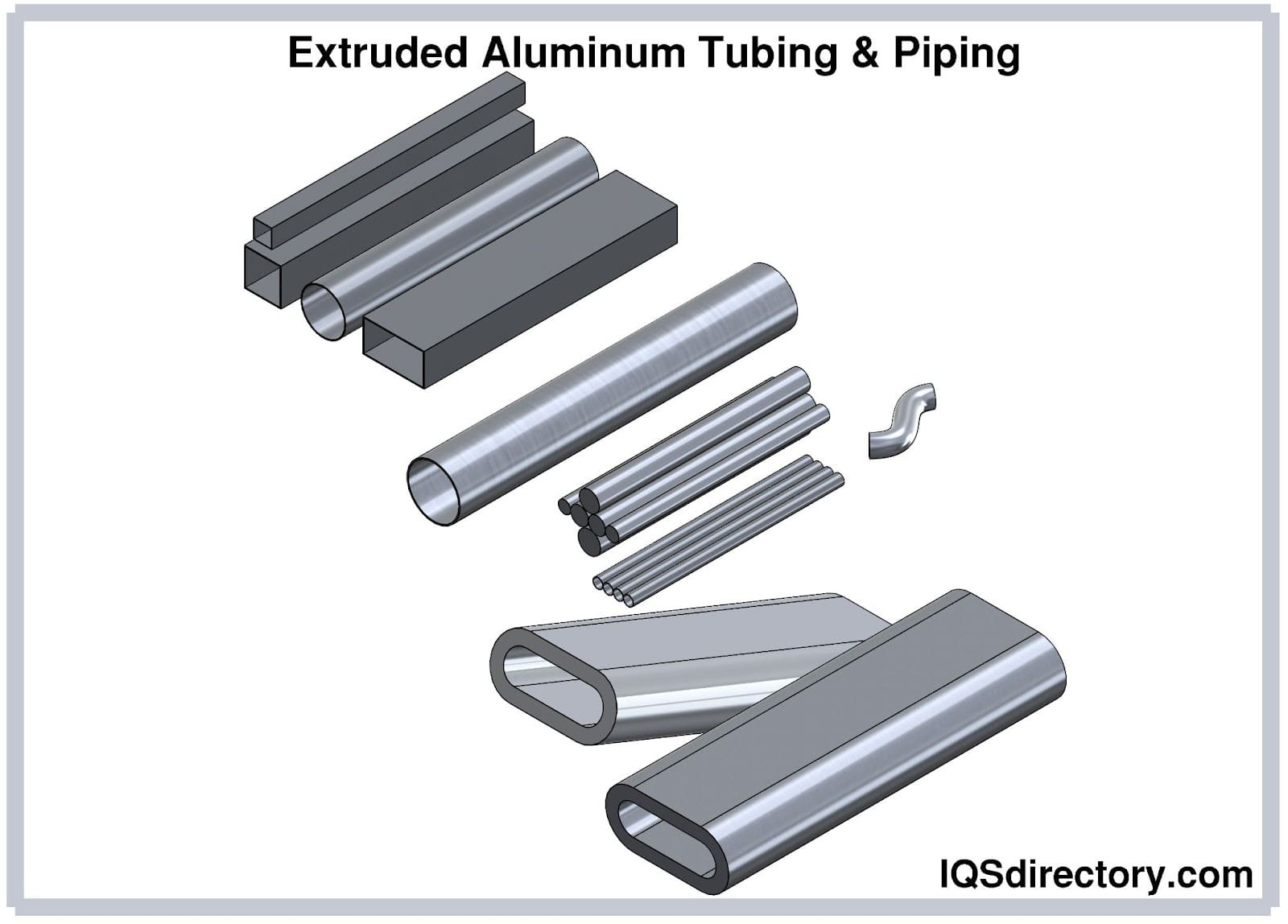
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services